Electric motor is used everywhere in industry and in term of technology,it is complex , sometimes making it a challenge to keep it running at peak performance.
Before motor fails we can do many things to suppress eventual failure or heavy damages. There are different reasons given below for failure of motor.
Before motor fails we can do many things to suppress eventual failure or heavy damages. There are different reasons given below for failure of motor.
1.Power Quality
- Transient voltage
- Voltage Imbalance
- Harmonic Distortion
2.Variable Frequency Drive
- Sigma current
- Reflections on drive output PWM signals
- Operational overload
3.Mechanical
- Misalignment
- Shaft imbalance
- Shaft looseness
4.Improper Installation Factor
- Soft foot
- Shaft voltage
Power Quality
- Transient
Transient may appear on control cables that don't necessarily cause equipment damage directly,but may disrupt operations.
- Voltage Imbalance
Three phase distribution systems often serve single phase loads, An imbalance in impedance or load distribution can contribute to imbalance across all three of the phases.
Please check voltage of each phase by using multimeter.
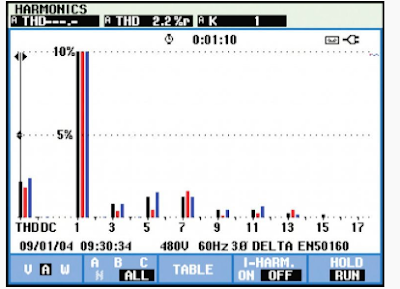
- Harmonic Distortion
These looses dissipate in the form of heat, which, over time, will deteriorate the insulation capability of the windings.some harmonic distortion of the current is normal on any part of the system serving electronic loads.
To start investigating harmonic distortion, use a power quality analyzer to monitor electrical current levels & temperatures at transformers to be sure that they are not overstressed.
Variable Frequency Drive
- Sigma Current
Sigma current find in motor cable.
The sum of the three currents would equal to zero. means the return current from the drive would be equal to the current to the drive. sigma current can also be understood as asymmetrical signals in multiple conductors that can capacitively couple currents into the ground conductor.
- Reflections on drive output PWM singals
VFD employ a pulse width modulation PWM technique to control the output voltage and frequency to a motor. Reflections are generated when there is an impedance mismatch between the source and load. Impedance mismatch can occur as a result of improper installation, improper component selection or equipment degradation over time, In a motor drive circuit, the peak of the reflection could be as high as the DC bus voltage level.
- Operational Overload
Motor component which are bearings, motor windings, and other components may be working fine, but the motor will continue to run hot. 30% motor fail because of overloading.
Mechanical
- Misalignment of a motor
Misalignment occurs when the motor drive shaft is not in correct alignment with the load,or the component that couples the motor to the load is misaligned. Many believe that a flexible coupling eliminates and compensates for misalignment, but a flexible coupling only protects the coupling from misalignment.
There are few types of misalignment:
1. Angular misalignment- shaft centerlines intersect but are not parallel
2. Parallel misalignment- shaft centerlines are parallel but not concentric
3. Compound misalignment- a combination of parallel and angular misalignment
- Shaft Imbalance
- Shaft looseness
Rotating looseness is caused by excessive clearance between rotating and stationary elements of the machine, such as in a bearing.
Non rotating looseness happens between two normally stationary parts, such as a foot and foundation,or a bearing housing and a machine.
Improper Installation Factor
- Soft foot
- Shaft voltage